Image Credit: Shutterstock
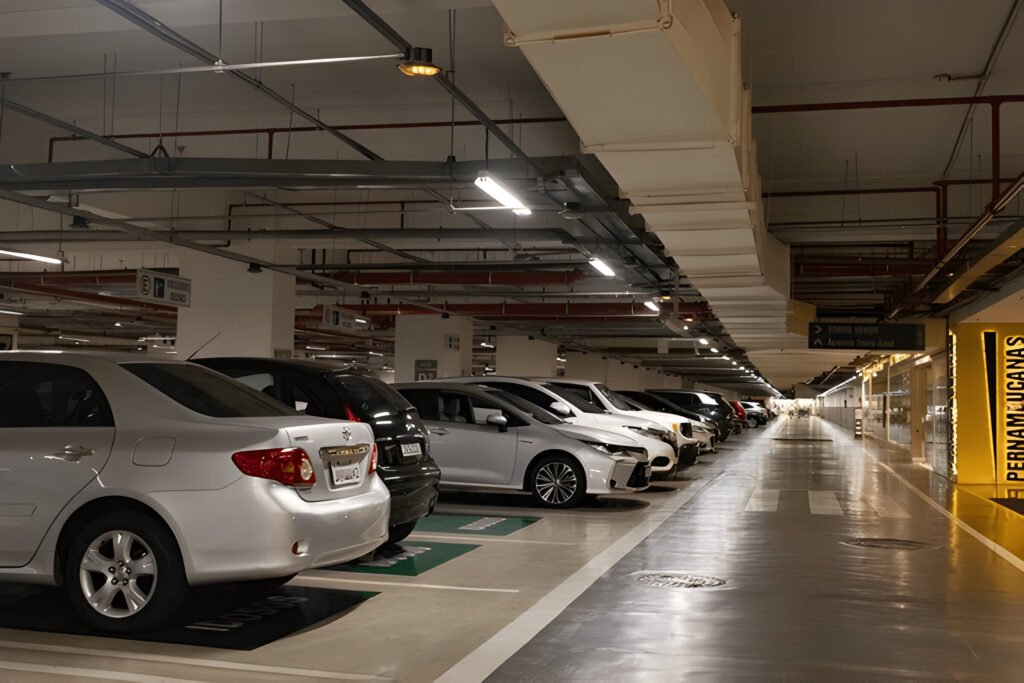

Facing the possibility of car repossession can be a stressful experience for vehicle owners. Understanding how to park your car to avoid repo has become a crucial concern for those struggling with loan payments. This guide aims to provide valuable insights into the legal aspects of repossession and practical strategies to protect your vehicle from being seized by a repo man.
Readers will learn about effective parking techniques to safeguard their cars, the importance of communicating with lenders, and potential alternatives to repossession. The article will also shed light on what happens when they repo your car and offer tips on how to stop a repo in progress. By exploring these topics, vehicle owners can gain a better understanding of their rights and options when dealing with the threat of repossession.
Understanding Vehicle Repossession Laws
Vehicle repossession laws vary from state to state, making it crucial for borrowers to understand their rights and the lender’s limitations. This knowledge can help vehicle owners navigate the complex process of repossession and potentially avoid losing their cars.
State-specific regulations
Each state has its own set of laws and regulations governing the repossession process. For instance, in Utah, lenders don’t need a court order to hire a repossession company to take a vehicle. This is known as self-help repossession. However, the process must be carried out without causing a breach of the peace. While Utah law doesn’t explicitly define what constitutes a breach of the peace, it typically includes actions such as entering a closed home garage without permission, breaking into locked areas, or using physical force.
In Massachusetts, lenders must send a written notice called “Rights of Defaulting Buyer under the Massachusetts Motor Vehicle Installment Sales Act” before repossession if a payment is missed. However, this requirement may be waived if the borrower has a history of late payments.
Your rights as a borrower
Borrowers have several rights during the repossession process. In many states, lenders can take a car as soon as the borrower defaults on the loan or lease. However, the lender can’t “breach the peace” when repossessing the vehicle. This means they can’t use physical force, make threats, or remove the car from a closed garage without permission.
After repossession, borrowers typically have a right to redeem their vehicle by paying the entire balance of the loan and all costs associated with the repossession. Some states also allow borrowers to “reinstate” their loan by paying the past-due amount plus the lender’s repossession expenses.
Borrowers also have the right to reclaim personal property found inside the repossessed vehicle. Lenders must hold these items for a certain period, which varies by state, and inform the borrower how to retrieve them.
Lender’s rights and limitations
Lenders have the right to repossess a vehicle when a borrower defaults on their loan. However, they must adhere to specific guidelines:
- Notice requirements: In some states, lenders must provide notice before repossession. For example, in North Carolina, while not legally required, some contracts may include a clause requiring prior notice.
- Repossession process: Lenders can typically repossess a vehicle from public areas or private property with public access, such as driveways or workplace parking lots. However, they can’t enter locked or enclosed spaces without permission.
- Post-repossession obligations: After repossession, lenders must provide written notice about their plans for the vehicle, including details about public auctions or private sales.
- Sale of the vehicle: Lenders must sell the repossessed vehicle in a commercially reasonable manner. They must apply the fair market value of the vehicle to the loan balance, even if the sale price is lower.
- Deficiency balance: If the sale price doesn’t cover the remaining loan balance plus repossession costs, the lender can pursue the borrower for the deficiency. However, some states have limitations on this right. For instance, in Utah, lenders can’t pursue deficiency balances for vehicles with an original cash price of $3,000 or less.
To wrap up, understanding vehicle repossession laws is essential for both lenders and borrowers. These laws aim to balance the rights of lenders to recover their collateral with the rights of borrowers to fair treatment during the repossession process. Borrowers facing potential repossession should familiarize themselves with their state’s specific laws and consider seeking legal advice to protect their rights.
Strategic Parking Locations to Avoid Repo
When facing the threat of vehicle repossession, strategic parking can play a crucial role in protecting one’s car. Understanding the legal boundaries and limitations of repossession agents can help vehicle owners make informed decisions about where to park their cars.
Private Property Considerations
Private property offers some level of protection against repossession. In many states, repo agents cannot legally enter locked gates or other locked property without the owner’s permission. This means that parking a vehicle inside a closed garage or a fully enclosed fence can make it more challenging for repossession agents to access the car.
However, it’s important to note that driveways are often considered fair game for repossession. Even if a driveway is on private property, it’s typically accessible to the public, making it a legal area for repo agents to operate.
One strategy some vehicle owners employ is to remain in the car when they spot a tow truck. It’s illegal for a tow company to repossess a vehicle with someone inside it. This tactic, while potentially effective, should be used cautiously and as a last resort.
Gated or Locked Areas
Gated communities and locked areas provide an additional layer of security against repossession. Repo agents cannot legally breach locked gates or use physical force to gain access to a vehicle. This limitation extends to cutting locks, chains, or causing any property damage, as these actions are considered a breach of peace in most states.
Key points to remember about gated or locked areas:
- Repo agents cannot enter locked gates without permission.
- Closed garages are off-limits for repossession.
- Open gates or garages may still be accessible to repo agents.
- Using force to enter locked areas is illegal for repo agents.
It’s worth noting that while these areas offer protection, they’re not foolproof. If a vehicle owner drives to a public location, such as a grocery store or workplace parking lot, the car becomes vulnerable to repossession.
Rotating Parking Spots
Another strategy to avoid repossession is to regularly rotate parking spots. This makes it more challenging for repo agents to locate the vehicle. Some tips for effective rotation include:
- Avoid parking in the same spot consistently.
- Use different parking locations within a neighborhood or area.
- Consider parking at friends’ or family members’ properties occasionally.
- Be mindful of public parking areas where the vehicle might be easily spotted.
It’s important to remember that while these strategies can make repossession more difficult, they don’t address the underlying issue of missed payments. Vehicle owners should prioritize communication with their lenders and explore options for catching up on payments or refinancing.
Lastly, it’s crucial to understand that hiding a vehicle or intentionally evading repossession can have legal consequences. Some lenders may view these actions as a breach of contract, potentially leading to more severe legal action.
In California, a specific law (AB 2210) protects consumers against illegal towing. If a vehicle owner spots a tow truck driver taking their car while still on private property, the driver must release the car unconditionally. Violations of this law can result in significant penalties for the tow truck operator, including fines and potential jail time.
While strategic parking can provide temporary protection, it’s not a long-term solution. Vehicle owners facing potential repossession should consider:
- Reviewing their loan agreement carefully.
- Communicating openly with their lender about financial difficulties.
- Exploring options for loan modification or refinancing.
- Seeking legal advice if they believe their rights have been violated.
By combining strategic parking with proactive communication and financial planning, vehicle owners can better navigate the challenges of potential repossession while working towards a more stable financial situation.
Communicating with Your Lender
When facing financial difficulties that affect one’s ability to make car payments, open communication with the lender becomes crucial. Early and honest dialog can lead to various solutions that help borrowers avoid repossession while allowing lenders to recover their investment.
Negotiating payment plans
One of the first steps a borrower should take is to reach out to their lender as soon as they anticipate payment issues. It’s essential to explain the circumstances causing financial strain and express a desire to keep the vehicle. Using a friendly tone, borrowers should be specific about their situation and ask to speak with someone who can assist with long-term solutions.
When negotiating, borrowers should:
- Be upfront about their financial situation
- Explain why the current payments are no longer affordable
- Propose a payment plan that fits their budget
- Be prepared for a potentially lengthy negotiation process
Lenders often prefer to work out a payment plan rather than go through the costly process of repossession. By offering to pay the wholesale value of the car, borrowers may find lenders more receptive, as this amount is comparable to what they would receive at a used-car auction after repossession.
Requesting temporary forbearance
For borrowers experiencing temporary hardships such as job loss, medical emergencies, or unexpected life changes, requesting forbearance might be an appropriate option. Forbearance allows borrowers to pause or reduce payments for a specified period.
To request forbearance:
- Contact the lender promptly, ideally before missing any payments
- Explain the nature of the hardship and its expected duration
- Inquire about the lender’s hardship programs and forbearance options
- Be prepared to provide documentation proving the hardship
It’s important to note that forbearance terms vary among lenders. Some may offer to skip or pause payments entirely, while others might only allow deferment of the principal while still requiring interest payments.
Exploring loan modification options
Loan modification can be a viable long-term solution for borrowers facing ongoing financial challenges. This option involves changing the terms of the original loan to make payments more manageable.
Steps to explore loan modification:
- Contact the lender and express interest in loan modification
- Submit a formal request in writing, including a detailed explanation of the hardship
- Provide all required documentation, such as proof of income and bank statements
- Be specific about how the modification will help maintain on-time payments
Loan modifications may include:
- Extending the loan term to reduce monthly payments
- Lowering the interest rate
- Temporarily reducing payments
When applying for a loan modification, borrowers should be honest about their ability to repay. Lenders typically require borrowers to demonstrate that they can meet the modified terms upon completion of the program.
It’s worth noting that not all lenders offer hardship programs or loan modifications. However, many have payment assistance options for borrowers in need. By being proactive and communicating openly, borrowers increase their chances of finding a solution that works for both parties.
Remember, lenders generally prefer to avoid repossession due to its costs and complexities. By approaching negotiations with a clear plan and demonstrating a commitment to repayment, borrowers can often find alternatives that allow them to keep their vehicles while addressing their financial challenges.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of potential car repossession requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding repossession laws, employing strategic parking techniques, and maintaining open communication with lenders, vehicle owners can greatly improve their chances of keeping their cars. These strategies have an influence on both short-term protection and long-term financial stability, giving borrowers more control over their situation.
To wrap up, while strategic parking and legal knowledge are helpful tools, the most effective way to avoid repossession is to address the root cause – missed payments. Open dialog with lenders, exploring payment plans, and considering loan modifications are crucial steps to take. By taking action and being proactive, borrowers can work towards a solution that benefits both parties and helps them keep their vehicles in the long run.
FAQs
1. How can I prevent my car from being repossessed?
To avoid repossession, you might consider catching up on late payments, reinstating the loan if you’re in default, redeeming the car by paying off the full loan balance, negotiating with your creditor, refinancing the car loan, or filing for bankruptcy to receive an automatic stay against repossession.
2. What are some methods to keep my vehicle hidden from repossession agents?
You could alter the car’s appearance, switch the license plate, park the vehicle at a different location such as a relative’s house, transfer the title to another person, or use the car sparingly without keeping it in predictable locations.
3. What occurs if the repossession agent cannot locate my vehicle?
If the repossession agent cannot find your vehicle, the creditor might opt for a replevin action. This involves filing a lawsuit to obtain a court order that mandates the return of the vehicle, which can be costly and legally demanding.
4. How can I legally block a repossession attempt?
Legally blocking a repossession can be achieved by filing for bankruptcy under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, which enacts an automatic stay preventing creditors from continuing with repossession efforts without court permission.
5. What should I do if a repossession agent is attempting to take my vehicle?
If faced with a repossession, ensure the agent has legal authority and is not breaching the peace. You can negotiate with the agent or contact your lender to discuss alternatives like payment plans. Also, documenting the event or contacting law enforcement if laws are being violated could be necessary. Lastly, consider removing personal items from the vehicle if repossession seems imminent.
6. Is it possible to stop a tow vehicle from repossessing my car?
The only guaranteed way to stop a tow vehicle from repossessing your car is by settling the outstanding balance or the full amount owed as demanded by the lender. Engaging calmly with the tow operator might help in understanding your options better.


One Comment