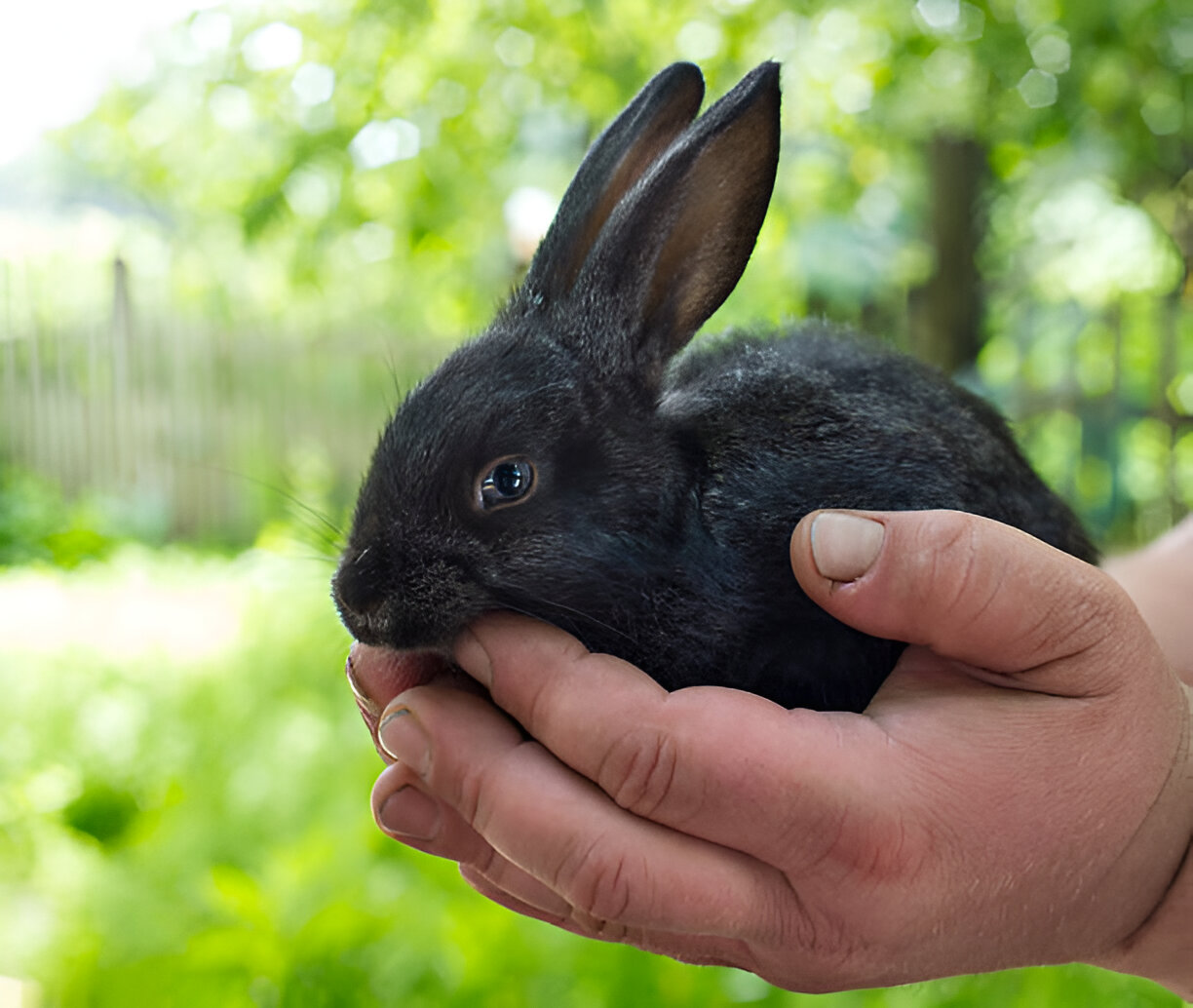
Determining the age of a baby rabbit can be a challenging task, especially for those unfamiliar with these adorable creatures. Whether you’ve found a wild cottontail or are caring for a newborn bunny, knowing how to tell how old a baby rabbit is can be crucial for its proper care and development. This skill is not only important for pet owners but also for wildlife enthusiasts and animal rescue workers who often encounter young rabbits in need of assistance.
To accurately assess a baby rabbit’s age, there are several key factors to consider. This article will explore the physical development milestones that indicate a bunny’s age, including fur growth, eye opening, and ear positioning. We’ll also discuss size and weight indicators that can help estimate how old a baby rabbit is. Additionally, we’ll delve into behavioral clues that can provide insights into a young rabbit’s age. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a better understanding of how to tell how old a wild baby rabbit or pet bunny is, enabling you to provide the best care possible.
Physical Development Milestones
Newborn to One Week
Baby rabbits, also known as kits or kittens, are born small, helpless, and without fur. They are blind, deaf, and rely entirely on their mother’s milk for nourishment. During the first week, their growth is influenced by factors such as litter size, birth weight, and temperature. By day 7, a fine layer of fur begins to grow, and the kits become more active and wiggly.
Two to Three Weeks
Around day 10, a significant milestone occurs as the kits’ eyes open, allowing them to start exploring their surroundings. By day 12, their ears open, enhancing their sensory abilities. The kits continue to grow rapidly, developing a full coat of fur by two weeks of age. They start showing interest in nibbling grass and herbage, although their mother’s milk remains their primary source of nutrition.
Four to Six Weeks
At this stage, the kits become increasingly independent. They regularly leave the nest and react to sounds by three weeks of age. Weaning begins around 4-5 weeks, with the introduction of small amounts of alfalfa hay and rabbit pellets. By 6 weeks, the kits look like miniature adults and are nearly fully weaned. They gain more strength and become playful and energetic, exploring their environment with growing curiosity.
Size and Weight Indicators
Weight Chart
Baby rabbits experience rapid growth in their early weeks. At birth, they typically weigh around 3-4 ounces. By 8-9 weeks, larger breeds like Flemish Giants can reach 5 pounds. From 8 weeks to 8 months, rabbits may gain 0.5 to 0.75 pounds per week. New Zealand white rabbits reach 6% of their 34-week weight by 2 weeks and 72% by 16 weeks.
Size Comparison
To assess a baby rabbit’s age, one can compare its size to common objects. If the bunny is smaller than a golf ball when cupped in hand, it’s likely very young. As it grows, it may become comparable to an extra-large egg. A healthy, releasable bunny should be able to sit up, making size comparisons easier. By 4-5 inches in length, the rabbit is nearing independence.
Growth Rate
A rabbit’s growth rate is influenced by factors such as litter size, birth weight, and temperature. Heavier babies tend to grow faster, possibly due to better competition for milk. Higher temperatures also promote faster growth. Interestingly, babies in larger litters may grow relatively faster at lower temperatures due to huddling behavior. Rabbits continue to grow until they are 6-9 months old, depending on the breed.
Behavioral Clues
Activity Level
Baby rabbits show distinct activity patterns as they grow. Newborns are mostly inactive, sleeping and eating. As they reach 2-3 weeks old, kits become more mobile and start exploring their surroundings. Young adult rabbits, typically 1-3 years old, display high energy levels, often zooming around and performing multiple binkies. They may be less willing to settle down when petted and are easily distracted. As rabbits age, their energy levels decrease. Middle-aged rabbits maintain a healthy activity level but are more prone to napping. Senior rabbits have low energy, preferring to rest most of the time.
Feeding Habits
A baby rabbit’s feeding behavior changes significantly as it grows. Newborns rely entirely on their mother’s milk, which is high in fat and protein but low in sugar. The mother typically feeds her babies for only 2 to 4 minutes every 24 hours, usually between midnight and 5 am. This feeding pattern stems from an instinct to avoid attracting predators. Around 3-4 weeks of age, kits begin to nibble on solid food, marking the start of the weaning process. By 4-6 weeks, they are usually fully weaned from their mother’s milk.
Independence
As baby rabbits grow, they become increasingly independent. In the early weeks, they huddle together in the nest, relying on their mother for warmth and nourishment. By 2-3 weeks, kits start moving around more actively. Their curiosity and independence continue to grow as they approach weaning age. Adult rabbits exhibit varying levels of independence based on their individual personalities. Some may be very independent, preferring to do things on their own terms, while others might become more attached to their favorite person, often the one who spends the most time with them and makes them feel safest.
Conclusion
Determining the age of a baby rabbit has a significant impact on providing proper care and ensuring its well-being. By observing physical development milestones, size and weight indicators, and behavioral clues, one can make an educated guess about a bunny’s age. This knowledge is crucial to implement appropriate feeding, housing, and handling practices, whether dealing with a wild cottontail or a domesticated pet rabbit.
Understanding how to gage a baby rabbit’s age empowers animal enthusiasts, pet owners, and wildlife rescuers to make informed decisions about its care. The ability to recognize age-related changes in fur growth, eye opening, and independence levels allows for tailored support during critical developmental stages. In the end, this expertise contributes to the overall health and survival of these adorable creatures, fostering a deeper appreciation for the intricate world of rabbit development.
FAQs
What are the characteristics of a rabbit at 3 weeks old? At three weeks old, a rabbit starts to develop a full coat of fur. Initially, baby rabbits are born without fur and begin to grow it around 3-4 days after birth. By the third week, they are usually fully furred.
Up to what age is a rabbit considered a baby? Rabbits are categorized as young from birth until 12 months. Specifically, they are considered babies or infants from birth up to about 3 months old. During this period, they primarily depend on their mother’s milk for sustenance.
How can you estimate the age of a cottontail rabbit? To gage the age of a cottontail rabbit, observe its physical development stages. If the rabbit’s eyes are closed, it is likely under 10-12 days old. Rabbits start to grow fur at about 3-4 days old, and they are fully furred by approximately 3 weeks.
Is a rabbit considered old at 10 years? A rabbit reaching 10 years is generally considered to be on the older side since the typical lifespan of a rabbit ranges from eight to twelve years. However, life expectancy varies with size, where smaller rabbits often live longer than their larger counterparts.